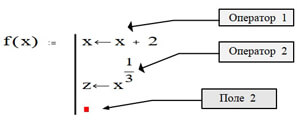
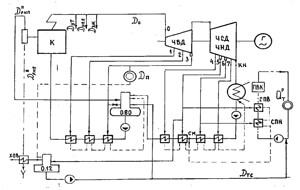
 Calculation of the thermal circuit of a heating power plant or boiler house with the determination of technical and economic indicators
Calculation of the thermal circuit of a heating power plant or boiler house with the determination of technical and economic indicators
This course involves developing an enterprise’s heat supply system or its individual components. Typically, the subject of the work is a combined heat and power plant (CHP), heating and industrial boiler houses. In some cases, it may also include the design of waste heat recovery units, workshop heating or ventilation systems, condensate collection systems, etc.
Key input data:
- CHP or boiler house construction location;
- electrical and thermal loads;
- turbine, boiler type, and capacity (if not specified by the student based on the assignment);
- fuel burned at the plant or boiler house;
- type of heating networks and network temperature curve;
- method for replenishing steam, condensate, and network water losses at the CHP or boiler house.
Additional input data required for the calculation are selected from recommended literature. These may include:
- number and parameters of turbine extractions;
- feedwater and network water temperatures;
- turbine section efficiency, boiler efficiency;
- deaerator and network heater activation method;
- The value of the heat production coefficient, etc.
The selection of the primary equipment for a planned CHP or boiler house is based on the required heat load, which can be determined by heat load schedules and heat consumption parameters.
Heat consumption schedules for process needs depend on production characteristics, equipment operating mode, technological processes, etc.
When creating heat load schedules, it is necessary to know the operating mode of the consumer equipment and the heat consumption standards per unit of output. The required heat consumption per year is determined for each consumer. The schedules are summarized using identical parameters for steam and hot water. When selecting the primary equipment for an industrial CHP or boiler house, the use of waste heat from the enterprises’ secondary energy resources should be taken into account. Construction and appearance of process heat consumption schedules for various energy-intensive industries