 Consumers and sources of heat production
Consumers and sources of heat production
When designing and operating thermal power plants, it becomes necessary to design new heat exchange equipment, or select and calculate standard heat exchange equipment, either for operation within the plant itself or for auxiliary purposes.
Depending on the problem to be solved, the use of one or another type of heat exchange equipment is appropriate.
To justify such a choice, both during course design and during graduation projects, it is necessary to develop not only schematic diagrams but also structural elements of systems and installations incorporating standard heat exchange equipment.
Therefore, this study provides examples of modern recuperative heat exchanger designs, indicating their geometric characteristics and other technical data necessary for design and calculation. Such information is also necessary when calculating and designing new heat exchange equipment, in order to compare the developed heat exchanger designs with existing ones.
CLASSIFICATION OF RECOVERY HEAT EXCHANGERS
A heat exchanger is a device for transferring heat from one heat transfer fluid to another. Heat exchangers used in industrial plants can be either directly integrated into process equipment or serve auxiliary purposes, such as supplying heat to a heat transfer fluid outside the heat-recovery unit or utilizing waste heat from spent heat transfer fluids.
By their operating cycle, heat exchangers are divided into continuous and intermittent heat exchangers.
For continuous heat exchangers, the primary mode is their steady-state operation. In this mode, the flow rates of both heat transfer fluids passing through the heat exchanger, as well as their initial and final temperatures, remain constant over time.
For intermittent heat exchangers, the primary mode is the transient mode. In this mode, the initial and final temperatures of one or both heat transfer fluids vary over time. Their flow rates may also change.
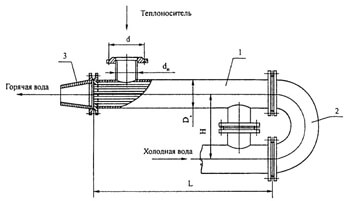
Recuperative heat exchangers (heat exchangers) are units in which heat transfer from one heat transfer fluid to another occurs through a separating wall. The heat transfer process consists of heat transfer from the heating fluid to the wall, thermal conductivity, and heat transfer from the wall to the heated fluid. There is no direct contact between the heat transfer fluids.
One of the most important stages in the design of thermal power plants is the selection of the type and size of the heat exchangers included in the plant.
At the earliest design stage, the designer should analyze existing standard designs and select the most suitable one. If a final decision cannot be made immediately, then it is advisable to consider several more or less suitable heat exchanger types during the initial design stage. In this regard, we will briefly review the classification and most common designs of standard recuperative heat exchangers.
Depending on the shape of the heat exchange surface, recuperative heat exchangers can be divided into those with a tube heat exchange surface and those with a sheet heat exchange surface. Heat exchangers with a tube heat exchange surface typically allow for significant pressure differences between the coolant fluids. Heat exchangers with a sheet heat exchange surface are, in some cases, more compact.
First, let’s analyze the main types of heat exchangers with a tube heat exchange surface.